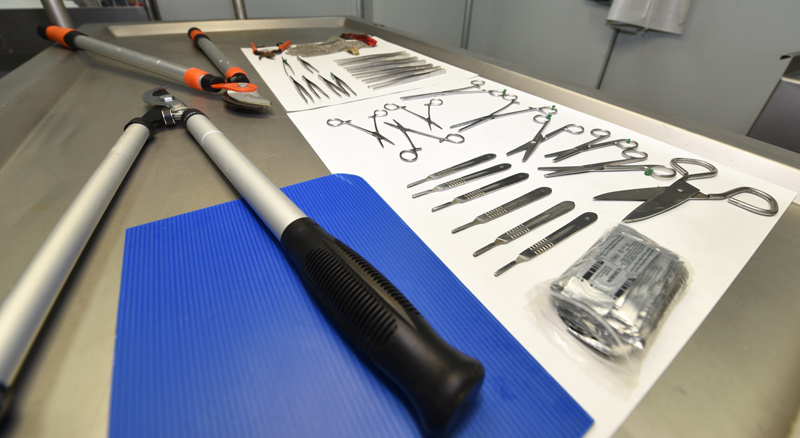
Necropsy instruments
The equipment has to allow the veterinary pathologist to take samples and study the cadaver without damaging the organs and tissues so that they can be evaluated later.
In addition, the material used in a field necropsy will not be the same as that used in a necropsy room, since in the first case, fewer elements will be necessary to carry out the sampling.
The material has to facilitate the veterinary pathologist the opening of the cadaver and sampling of the tissues and organs. Most of them are made of stainless steel.
The instruments are classified according to their purpose and use:

Cutting material
- Electric saw to cut the cranial vault, otherwise a saw.
- T-shaped chisel, to detach the cranial vault.
- Scalpel handle with disposable blades.
- Knives of different lengths depending on their use: 140 mm (for boning), 160 mm (cutting), 210 mm (quartering).
- Costotome, for cutting the ribs.
- Scissors with blunt and fine blades, for opening bile ducts and small arteries, and blunt-bladed scissors (Metzenbaum), for opening longitudinal organs (intestine). Both types of scissors can be curved or straight.
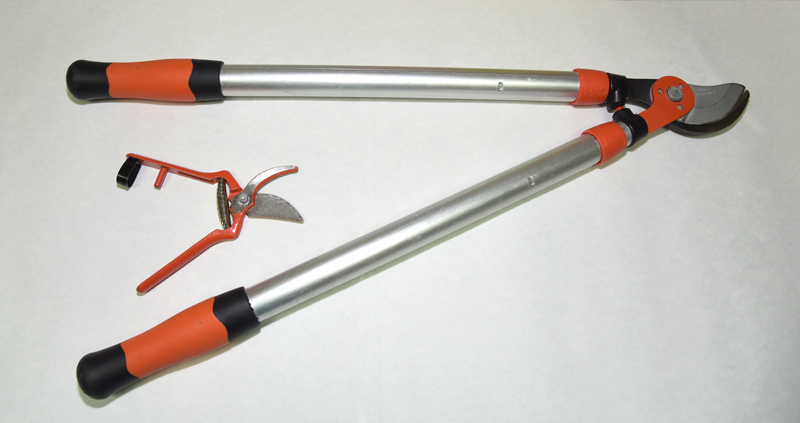


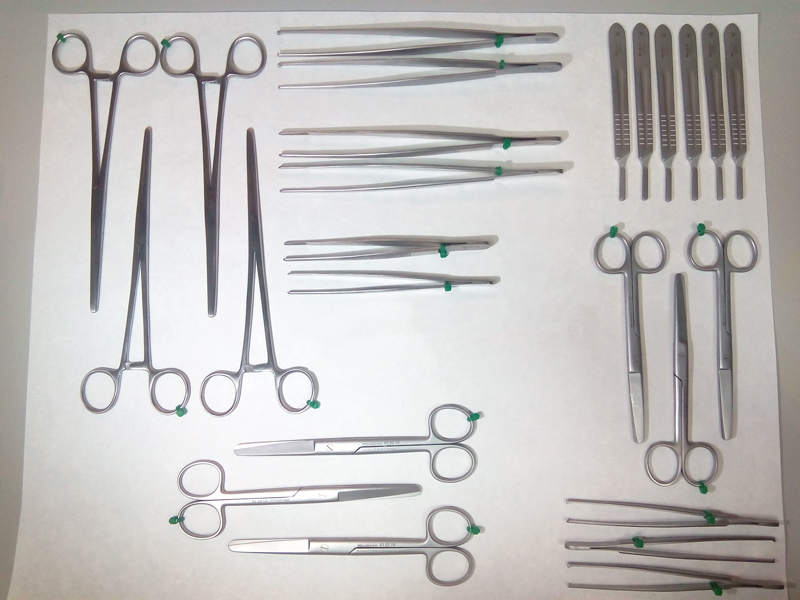
Material for grasping
- Dissecting forceps or elastic grasping forceps. The use of these forceps is determined by their tip. Toothless forceps will be used to manipulate tissues without damaging them. Forceps with teeth for grasping tissues that need more pressure and do not need to be preserved in perfect condition.
- Continuous pressure forceps for grasping and mobilization of soft tissues. This type of instrument is known as a clamp, which can have a wide or reduced blade, as in the case of the mosquito. An example of their use is the closure of longitudinal organs from the interior of which contents may come out, as in the case of the esophagus.
Recording material
- Camera with macro lens for detailed photography. If possible, video camera (zenithal and first person). The use of a tripod is recommended as it will provide stability and a good angle for photography.
- Colored photographic background (black/green/blue) to take the photographs.
- Measuring tape.
- Scale.
- Indelible markers, pens and pens.
- Necropsy template to write down in an orderly, complete and systematic way the findings of the necropsy.
Cleaning material
- During the necropsy it will be necessary to clean the material. Generally, 3 jars will be used: one with soap and water (1:1), one with bleach and, finally, one with water to rinse the material.
- Bio-sanitary container.
- Wick paper roll.
- Vegetable paper.
- Thin and thick gauge garbage bags.
- Bio-sanitary containers for the disposal of sharps (blades, needles, etc.).

Containers and equipment for preservation of samples
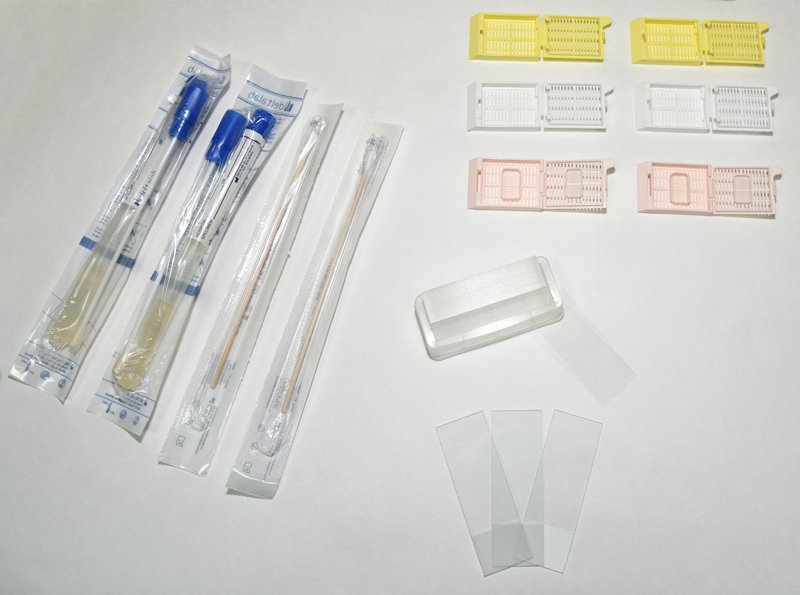
- Plastic bags with hermetic seal (zip type bags).
- Plastic jars with snap-on and screw-on lids for use with 10% formaldehyde, of different dimensions depending on the size of the organ sample to be collected.
- Falcon type jars.
- Duchess type jars (sterile or not), if the organs are collected for toxicology or microbiology.
- Swabs with medium and without medium.
- Cassettes to introduce the organs in 10% formaldehyde solution once carved (in case it is done during the necropsy).

Fijador
Formaldehyde (10%), stabilized with methanol. Currently, there is a tendency to use other fixatives as substitutes for formaldehyde: Tisssue-Tek Xpress Molecular Fixative®, Fine FIX Concentrate® o Greenfix®
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
In addition to the working material, the veterinary pathologist needs protective equipment (Personal Protective Equipment - PPE) that will be more or less restrictive depending on the suspicion of the death of the animal. In general:
- High-top rubber boots that allow easy cleaning.
- Sanitary coat and pants.
- Waterproof gown or, failing that, plastic apron and waterproof sleeves.
- FFP2 type mask.
- Safety/splash goggles or, failing that, full face shield.
- Headgear to protect hair.
- Nitrile gloves.
- Anti-cut glove (mesh glove).
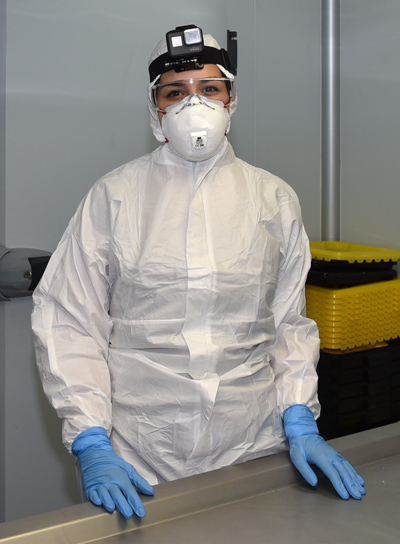

For zoonotic diseases or diseases that require a high level of control to prevent their spread, it will be necessary to replace the gown or apron with a full-body coverall with hood. The mask in this case should be FFP3 type. This type of necropsies, if possible, should be performed in a fully controlled environment and under the most restrictive safety measures (such as in a safety level 3 laboratory).

